What Are the 3 Key Functions of the Teeth? Vancouver Centre for Cosmetic and Implant Dentistry
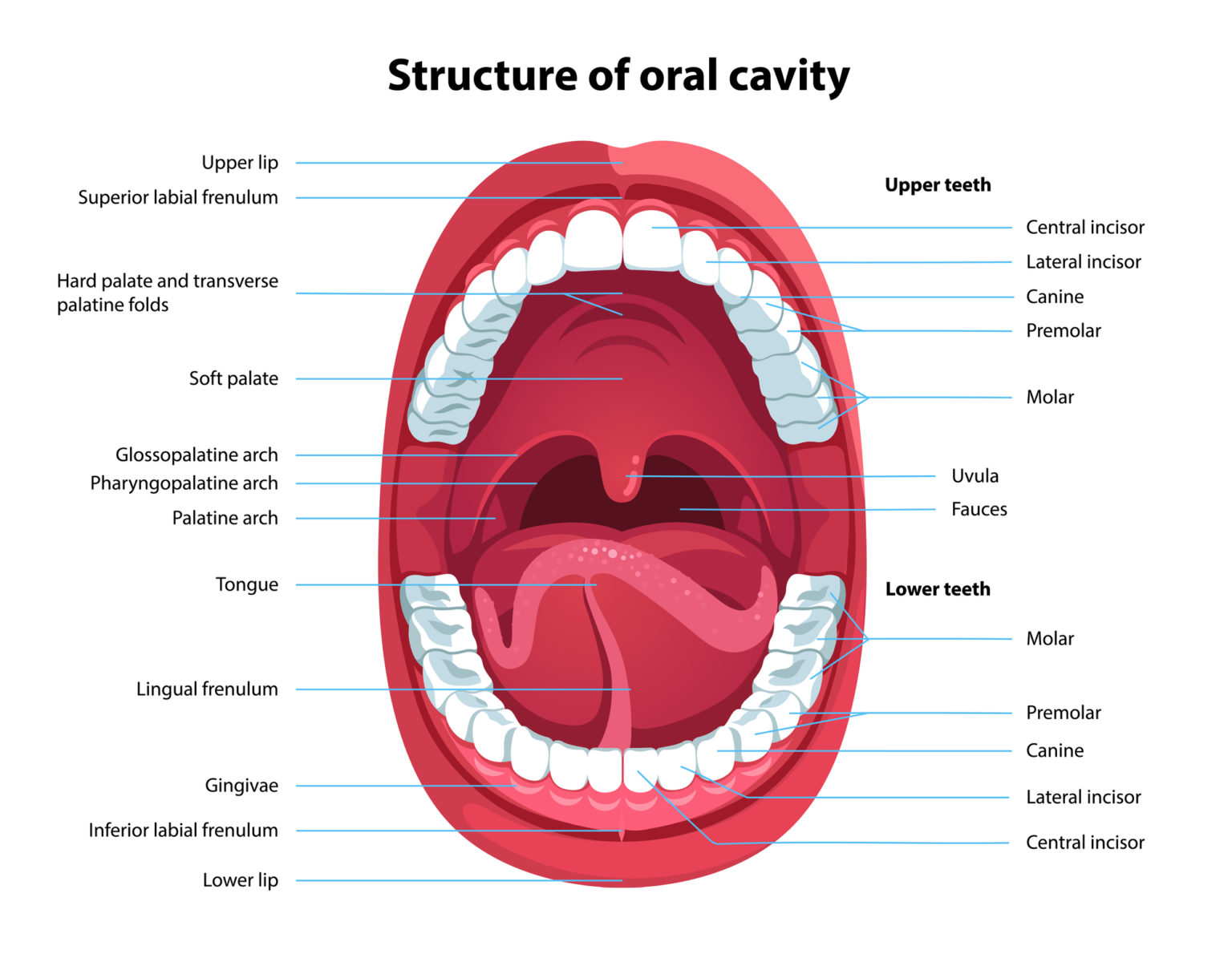
Human Mouth - Description The mouth or oral cavity is the beginning of the human digestive system, and it can be divided into 2 portions - the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule comprises the lips, cheeks and teeth. The oral cavity proper includes the tongue.

Mouth Anatomy 11 Different Human Mouth Parts and their Functions (with Examples) Love English
The oral cavity, or more commonly known as the mouth or buccal cavity, serves as the first portion of the digestive system. It consists of several different anatomically different aspects that work together effectively and efficiently to perform several functions. These aspects include the lips, tongue, palate, and teeth. Although a small compartment, the oral cavity is a unique and complex.
Mouth anatomy Castle & Spark
Your mouth — also known as the oral cavity — shapes the appearance of your face and helps you eat, speak and breathe. It takes many parts working together to handle so many important jobs. Get to know the functions of the different parts of your mouth, and you'll gain a greater appreciation for the importance of great oral health.

23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus Anatomy & Physiology
A closed human mouth. The lips come together to close the opening of the mouth, forming a line between the upper and lower lip. In facial expression, this mouth line is iconically shaped like an up-open parabola in a smile, and like a down-open parabola in a frown.
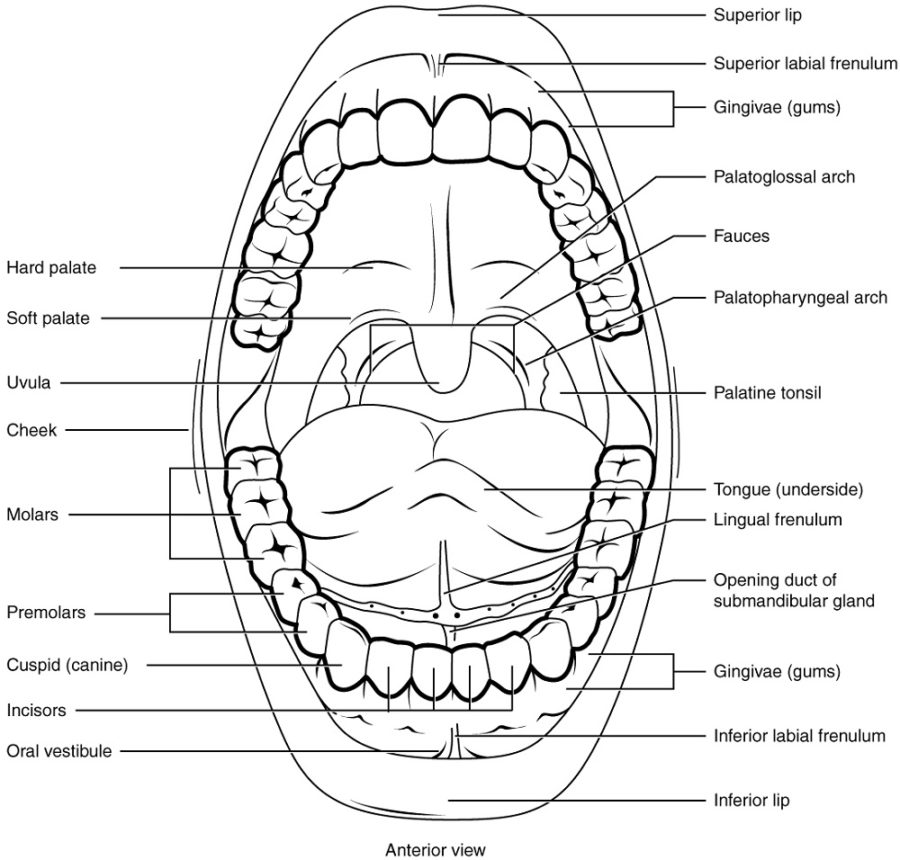
Diagram of the Mouth 101 Diagrams
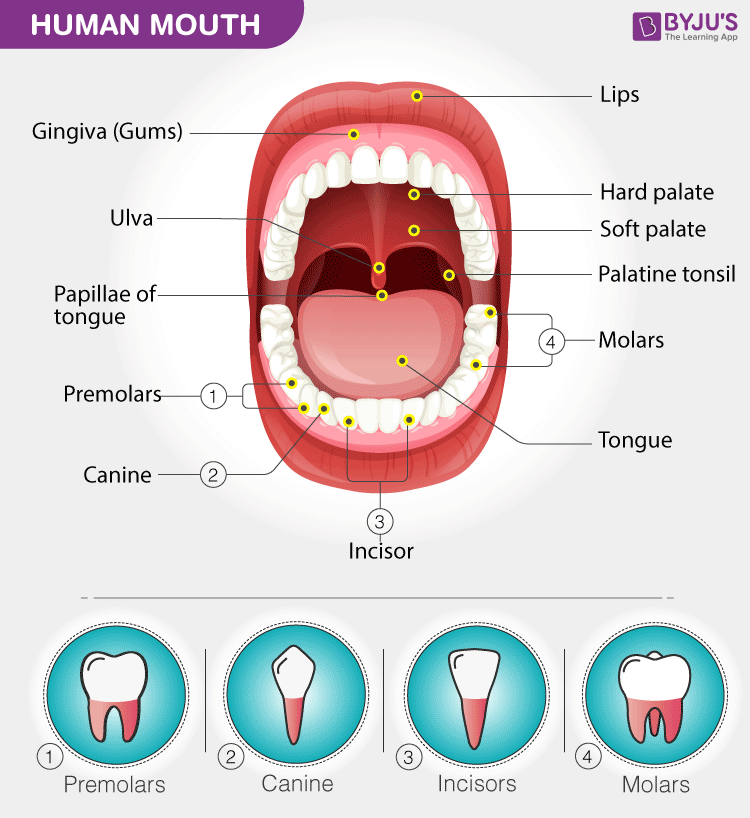
Structure of Human Mouth. The mouth contains some of the strongest muscles in the human body. One of these muscles is the tongue. The tongue is the pound for pound strongest muscle a human possesses. It is also the only muscle that is only attached at one end. Looking inside the mouth we can see the following: Lips. Lips form the border of our.
The Mouth and Buccal Cavity Anatomy of the Human Mouth
Oral vestibule Vestibulum oris 1/2 Synonyms: none The cavity is separated into anterior and posterior parts by the dental arches (or teeth): the anterior oral vestibule sits anteriorly to the teeth and behind the lips, whilst the oral cavity proper describes the area behind the teeth.

Mouth Teeth Diagram with Label coordstudenti
What's my mouth's function? Your mouth supports many daily functions, including: Breathing. Talking. Chewing. Tasting. Swallowing. Eating. Drinking. Mouth function in digestive system Your mouth is where digestion begins. When you chew food, your salivary glands make saliva (spit). Saliva helps break down starches in the foods you eat.
Mouth and Stomach Part 2 and 3 of the 5 Phases of Digestion
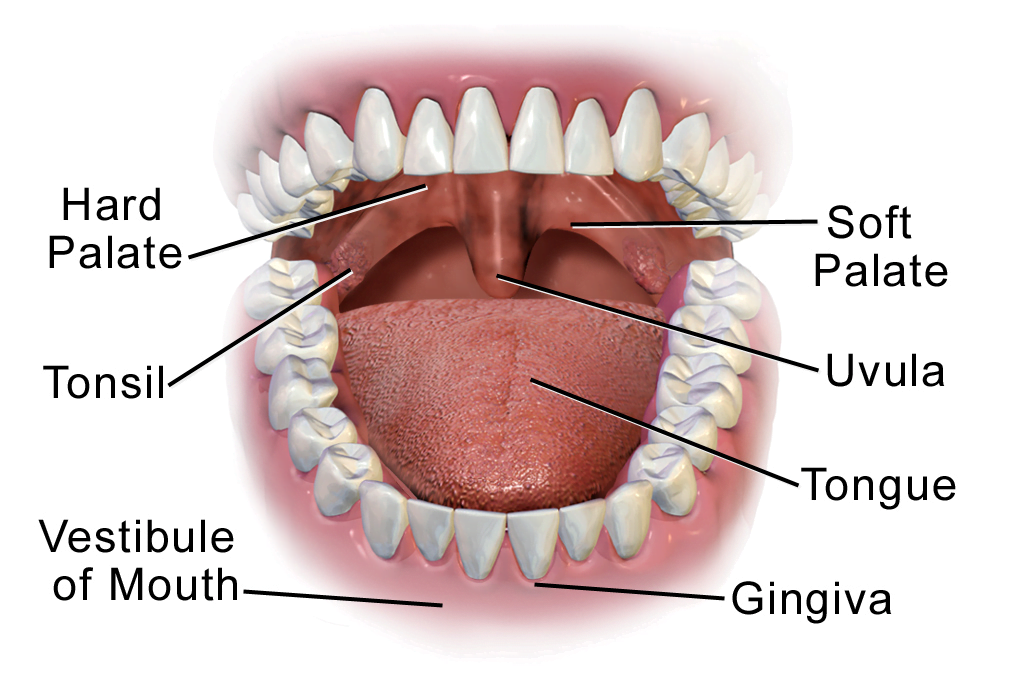
Anatomy of a Mouth The mouth (oral cavity) consists of several components, including the teeth, gingiva (gums), tongue, palate, cheeks, lips and floor of the mouth. With the exception of the teeth, the mouth is lined by mucous membranes. The Teeth
1 Oral Structures and Tissues Pocket Dentistry
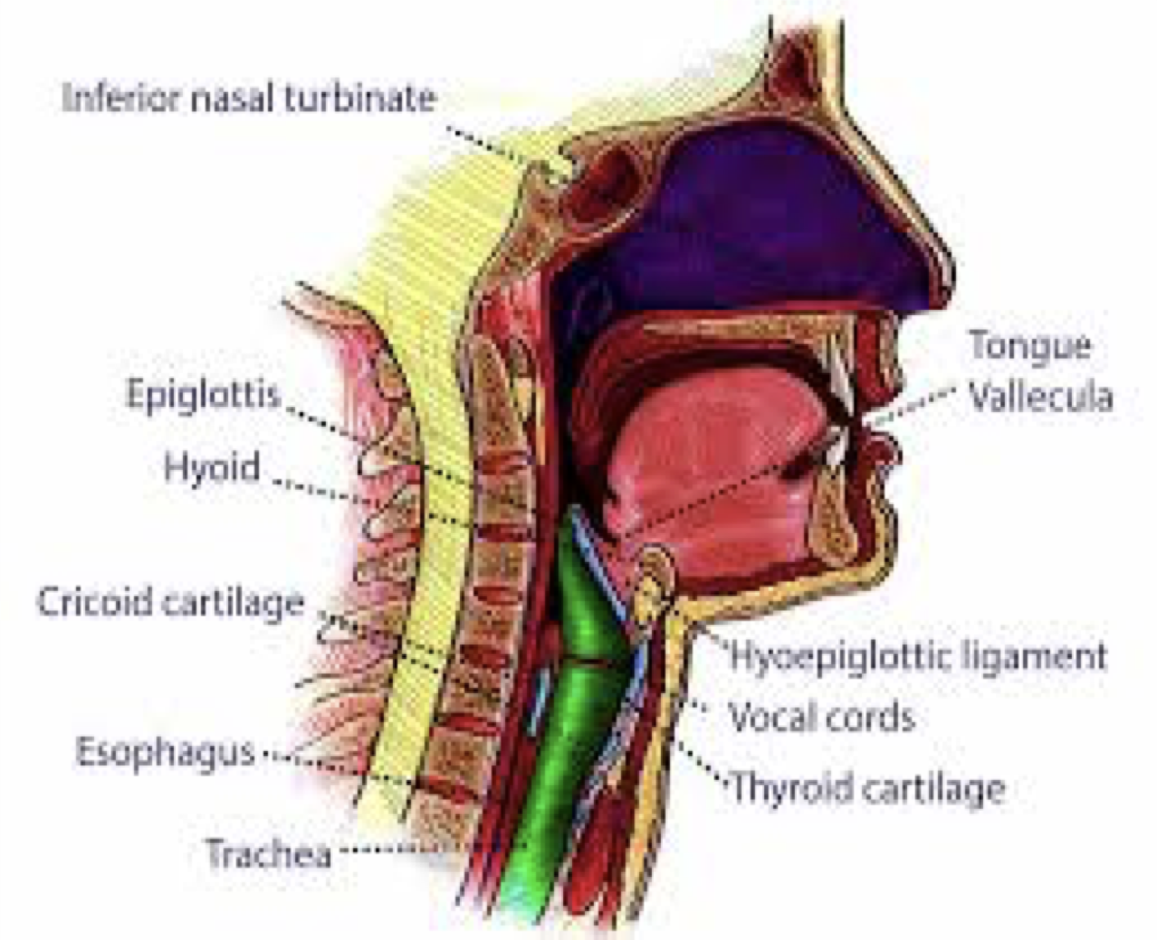
In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity).

Tooth and Mouth Anatomy How Do These Contribute to Good Health?
The Mouth By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: Feb 16, 2022 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom + − Click To View Large Image Also known as the oral cavity, the mouth is the hollow cavity that allows food and air to enter the body.
Mouth diagram Healthiack
We have created 110 medical original illustrations of the mouth, the buccal cavity, the bones of the palate, the tongue, the salivary glands and the oral part of the pharynx with vessels and nerves.

Anatomy Of Mouth Anatomy Of Oral Cavity Human Anatomy Diagram Oral Anatomy Of The Mouth
In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity).

Detailed mouth anatomy
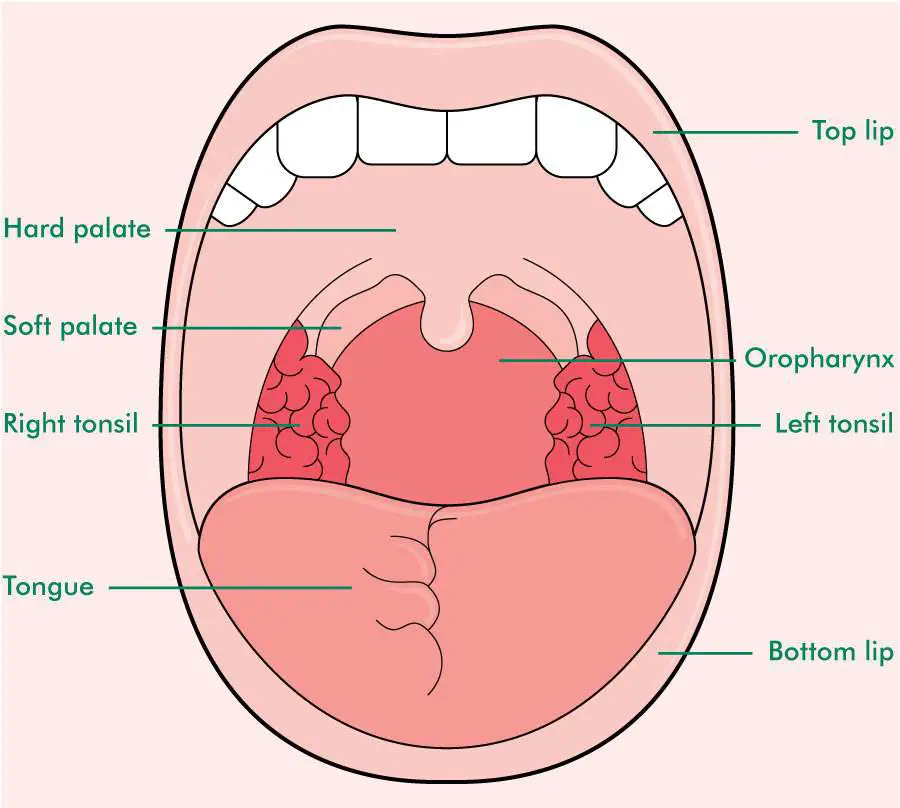
Uvula What is the mouth? The mouth, also called the oral cavity, is the opening in the human skull that allows food, liquids, and air to enter the body. The oral cavity begins at the lips and.
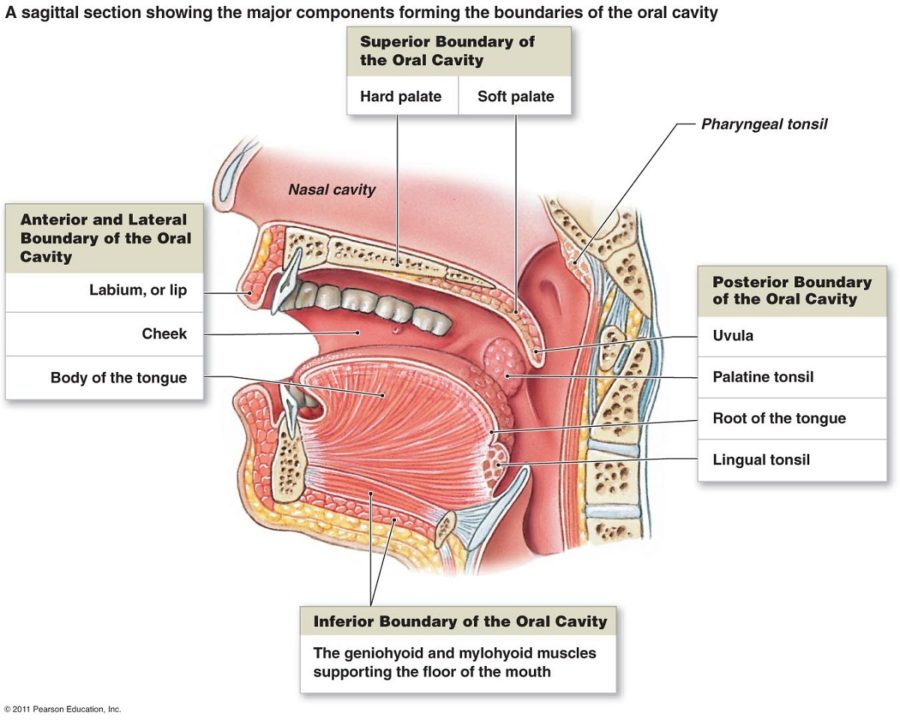
Diagram of the Mouth 101 Diagrams
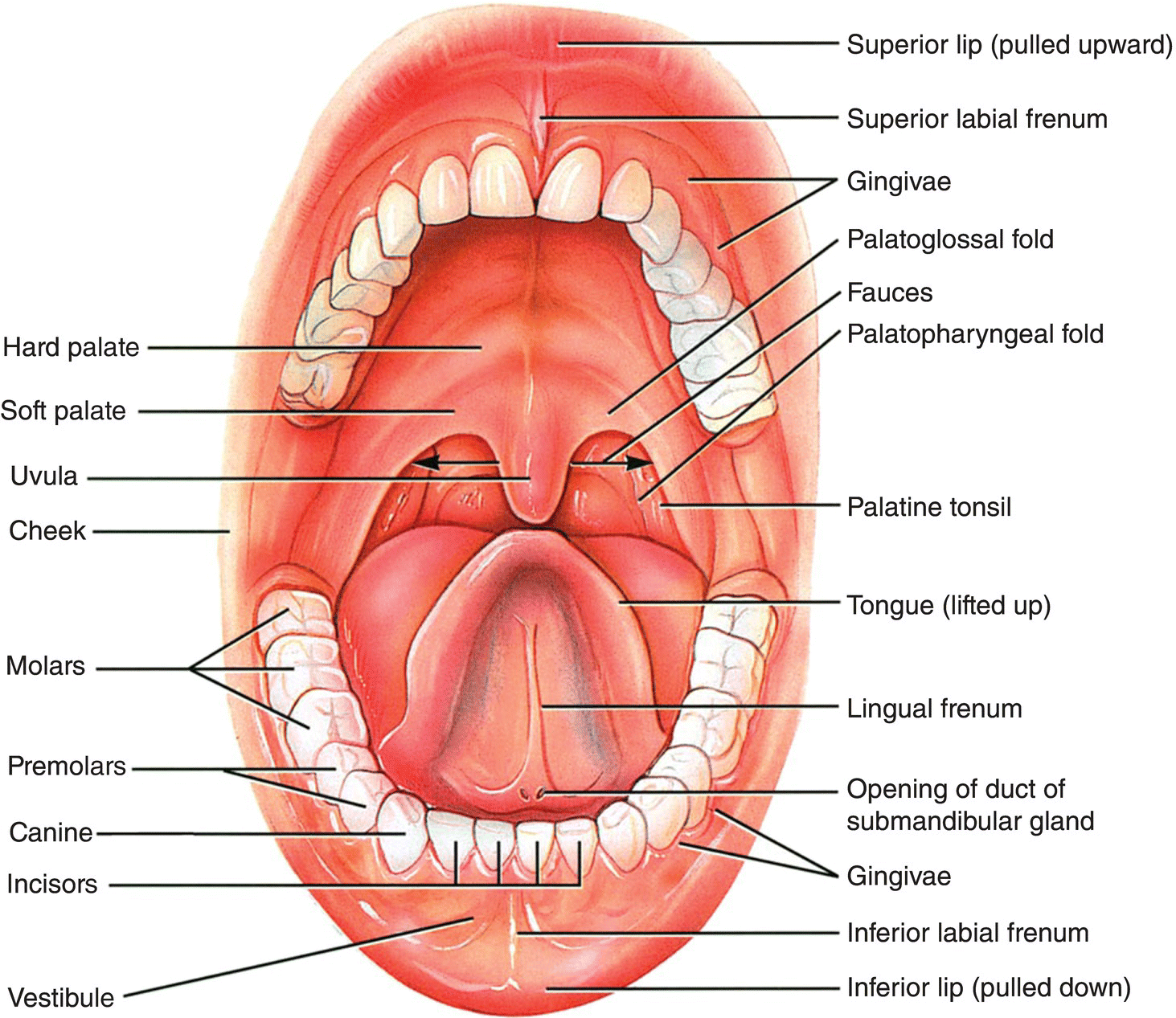
Fig 1 - The two divisions of the oral cavity are the vestibule and oral cavity proper. Mouth Proper The mouth proper lies posteriorly to the vestibule. It is bordered by a roof, a floor, and the cheeks. The tongue fills a large proportion of the cavity of the mouth proper. Roof The roof of the mouth proper consists of the hard and soft palates.

Human Mouth Anatomy, Open Mouth With Explaining Stock Photo 377986870 Shutterstock
The structures of the mouth are illustrated in. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper. Lips are very vascular with a thin layer of keratin; hence, the reason they are "red."

Diagrams of the Mouth 101 Diagrams
The boundaries of the oral cavity include the hard palate and soft palate that form the roof of your mouth, the tongue and the muscles below it, which make up the floor of the mouth and the inner surface of the lips in the front, the cheeks on the sides, and the uvula (the little "punching bag" shaped structure) at the end of your soft palate in.